China's Covert Support for Russia in Ukraine War
As the war in Ukraine rolls into its fourth year, China's role has come under increasing international probing.
While Beijing publicly maintains a stance of neutrality, evidence suggests that China has been providing substantial indirect support for Russia’s military efforts, prompting criticism from Western nations and raising concerns about the conflict’s direction.
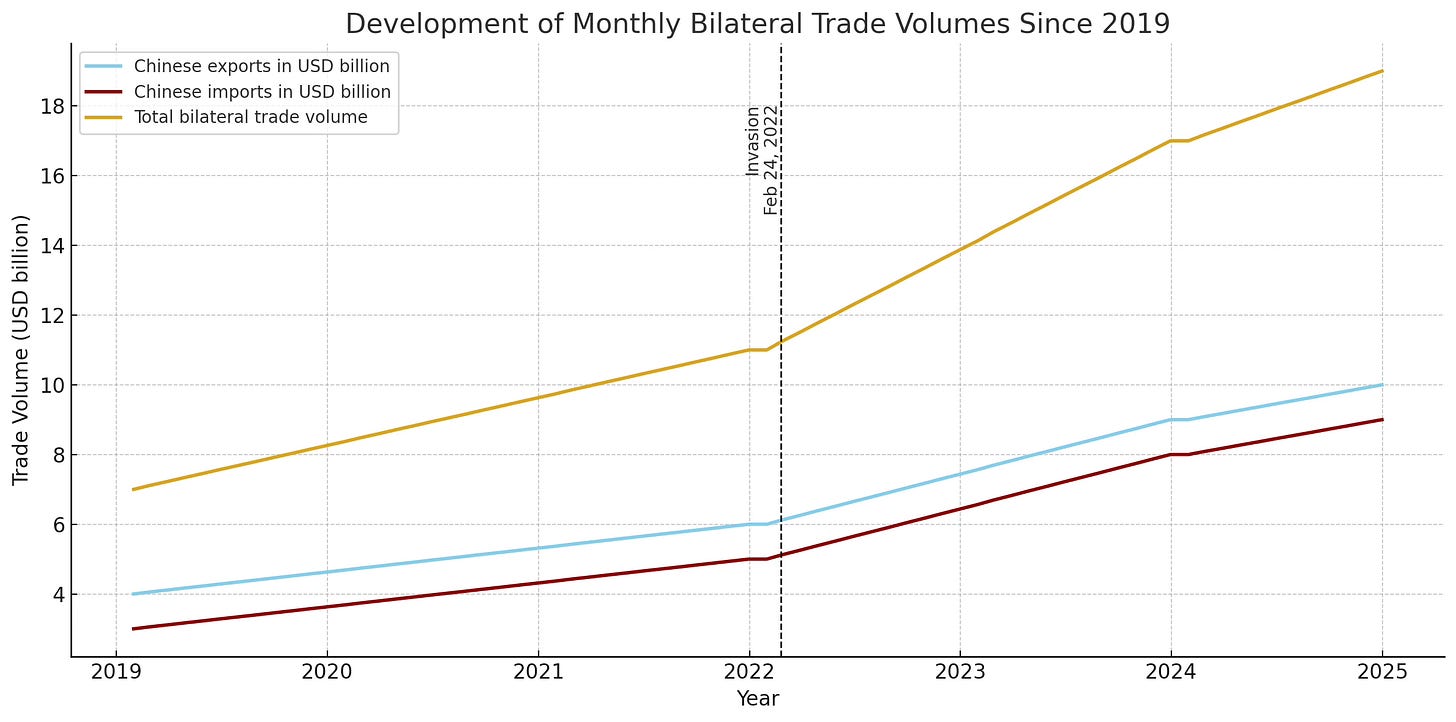
China has proved a critical partner for Russia, especially in the wake of Western sanctions. In 2023, bilateral trade between the two countries soared. China has significantly increased its purchases of Russian oil and gas, becoming Russia’s top crude oil customer in 2023. This economic partnership has provided Moscow with a vital revenue stream in a bid to sustain its military operations in Ukraine.
Beyond economic ties, China has been accused of supplying Russia with dual-use technology civilian goods that can be repurposed for military use. U.S. officials have reported that China has provided Russia with components for drones, cruise missiles, and other military equipment. Notably, around 80% of critical electronic components in Russian drones were traced back to China in early 2025. Additionally, Chinese-made trucks and microelectronics have been instrumental in bolstering Russia’s logistics and weapons production capabilities.
The G7 nations have condemned China’s support for Russia, stating that such actions enable Moscow to continue its assault on Ukraine. In response, the U.S. Senate is considering 500% tariffs on countries importing Russian energy products, aiming to isolate Russia economically. This legislation specifically targets key markets like China and India that fund Russia’s war efforts.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has publicly criticised China’s role in the conflict, accusing Beijing of supplying key equipment and supplies to Russian defence manufacturing facilities. Zelenskyy revealed that during a phone call in April 2023, Chinese President Xi Jinping promised not to support Russia with weapons. However, subsequent intelligence reports indicated that elements of Russia’s weaponry were sourced from China, leading to a deterioration in diplomatic relations between Kyiv and Beijing.


Analysts suggest China’s involvement is prodiminantly driven by strategic interests. Beijing seeks to prevent a total Russian defeat, which could lead to a pro-Western regime in Moscow, while also avoiding direct confrontation with the West. This balancing act reflects China’s aspirations in reshaping the global order and reducing Western dominance, even if its means indirectly supporting Russia’s war efforts.
Sources:



